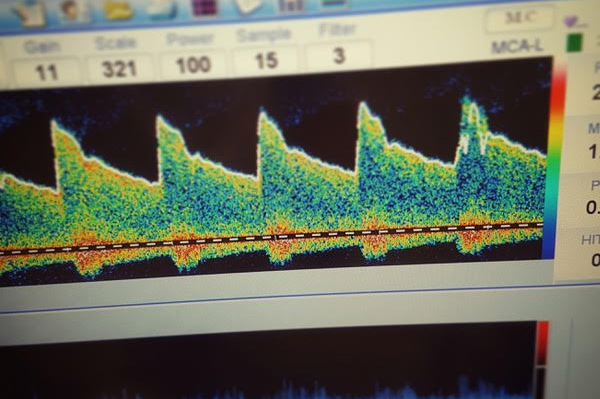
- To provide important information and help diagnose and determine the best treatment for stroke or stroke warning signs
- To evaluate blood flow in the brain and the major arteries and veins of the neck, arms and legs
To identify abnormalities, such as narrowing (vasospasm), blockages, or arteriovenous malformation (a congenital blood vessel defect), in arteries within the brain.
- To monitor progression of cerebral vasospasm
- Detection and follow-up of stenosis or occlusion in a major intracranial artery in the
circle of Willis and vertebrobasilar system, including monitoring of thrombolytic therapy for acute stroke patients.
- Detection of cerebral vasculopathy.
- Detection and monitoring of vasospasm in patients with spontaneous or traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Evaluation of collateral pathways of intracranial blood flow, including after intervention.
- Detection of circulating cerebral microemboli
- Detection of right-to-left shunts
- Assessment of cerebral vasomotor reactivity
- As an adjunct in the confirmation of the clinical diagnosis of brain death
- Intraoperative and periprocedural monitoring to detect cerebral embolization, thrombosis, hypoperfusion, and hyperperfusion
- Evaluation of sickle cell disease to determine the stroke risk.
- Assessment of arteriovenous malformations
- Detection and follow-up of intracranial aneurysms
- Evaluation of positional vertigo or syncope
A technologist will ask you to recline in a chair or lie on a bed. You will be asked to move into different positions during the test. It is important to do exactly as the technologist tells you. A gel that washes off with water will be put on different areas of your scalp. Ultrasound does not travel well through air, so the gel is used to keep air bubbles from blocking the sound waves.
Usually 3 areas of your head are tested: your temples, your closed eyes, and the back of your skull. You may feel a slight pressure as the transducer is moved over these areas. The transducer makes blood flow audible. During the test, you may hear sounds of the blood flowing through your arteries. The technician will adjust the sound volume of the speaker to locate the blood vessels to be studied. The test usually lasts 15 to 20 minutes.
Your patient's exam will be interpreted by a board certified radiologist, who dictates a report. You will then receive your results within 48 to 72 hours.