Peripheral Vascular Disease
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) refers to diseases of blood vessels outside of the heart and brain. It is often a narrowing of vessels that carry blood to the legs, arms, stomach or kidneys. Varicose veins are an example of PVD in the veins.
The most common type of PVD occurs in the arteries. This is called peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which like coronary artery disease, occurs as a result of plaque or fatty buildup (atherosclerosis) in the walls of the arteries. This may include an aneurysm ballooning the arterial wall within the abdominal section of the aorta or carotid artery disease.
PAD may be dangerous if left untreated and could result in gangrene and amputation of limbs due to severely restricted blood flow. Some patients with PAD have a higher risk of stroke or heart attack. Early detection of PAD is essential.
Symptoms of PVD
- Cramping or fatigue in the legs while walking, called ‘claudication’
- Swelling or edema in lower extremities
- Non-healing sores on the feet or legs
- Pain in the feet while in bed, restless legs
- Numbness and tingling in the feet or hands
- Severe or sudden abdominal and/or back pain (abdominal aortic aneurysm)
- High blood pressure or blood pressure that is hard to control with medications (kidney arteries)
Carotid Artery Disease
The carotid arteries supply the head and neck with oxygenated blood. Carotid artery disease refers to the narrowing of these arteries caused by the build up of plaque (fatty substances along the inner wall of the artery). Since carotid arteries supply blood to the brain there is a risk for stroke when the arteries are narrowed.
Symptoms of Carotid Artery Disease
- Sudden weakness, tingling or numbness on one side of the face or body.
- Sudden confusion, dizziness, or difficulty speaking.
- Sudden blurred vision or difficulty seeing out of one or both eyes.
- Sudden severe headache.
- Sudden loss of balance, difficulty walking.
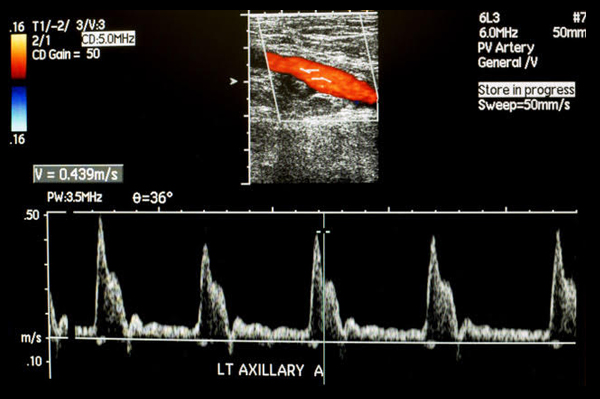
The test is done while you are lying on your back. Ultrasound gel is placed on your leg that allows the ultrasound signals to travel to the arteries. The technologist will use a transducer over the gel to visualize the arteries. The ultrasound waves will bounce off of the blood vessels and travel back to the transducer, which produces the image on the ultrasound machine. The technologist can then visualize any area of narrowing in the artery and take measurements of the blood flow. You will hear a “swooshing” sound when the Doppler is turned on which represents your blood flow.
You do not need to do anything to prepare for this test.
This test is also a good way to monitor known lower extremity arterial narrowing and to follow up on vascular surgery to the legs such as bypass surgery, angioplasty, and stents.
Your patient's exam will be interpreted by a board certified radiologist, who dictates a report. You will then receive your results within 48 to 72 hours.